Near San Miguel de Allende, Guanajuato, Mexico — The Central Highlands (North America)
Cañada de la Virgen: A Ceremonial Civic Center in the Laja River Basin Marker
Inscription.
Cañada de la Virgen: un centro cívico ceremonial en la Cuenca central del río Laja.
En la epoca prehispánica Cañada de la Virgen fue un centro cívico ceremonial que alcanzó su mayor desarrollo durante los años 540 a 1050 d.C. En las excavaciones se encontraron materiales procedentes de las costas del océano Pacífico y el Golfo de México, el Occidente y la Cuenca de México. En la abundante cerámica encontrada predomina el tipo blanco levantado y los tonos anaranjados que se relacionan con las tierras bajas queretanas y los valles del Hidalgo.
Aquí se veneraba a los dioses y ancestros, se estudiaba a los astros, principalmente la luna, el sol y venus, a partir de su registro y observación se determinaban los calendarios que regían la vida ceremonial, así como el manejo de los ciclos de intercambio con la naturaleza y las actividades productivas como agricultura, caza y recolección.
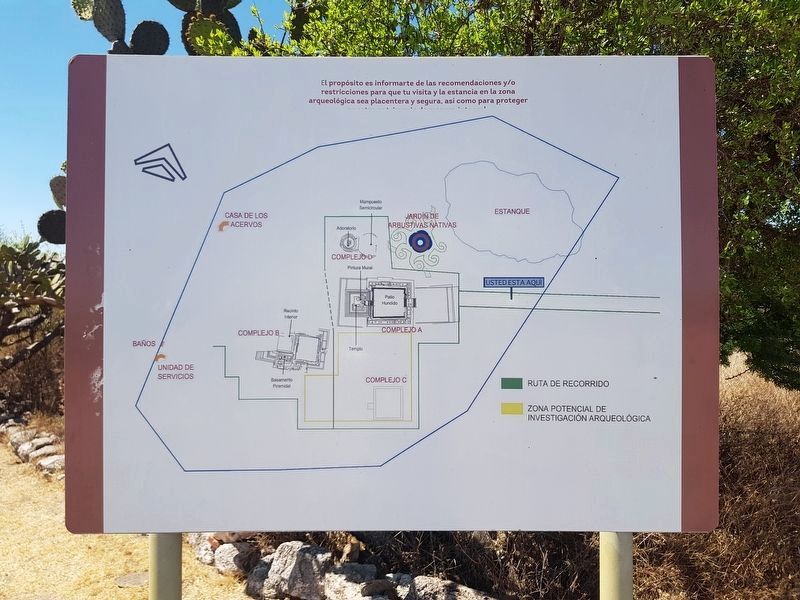
Cañadas de la Virgen se encuentra sobre una meseta rodeada de cañadas sobre las que descansa un estanque que debió ser estratégico para la fundación del lugar, pues con el agua y los variados recursos del ecosistema de mesetas, cañadas y valles, se tenía lo necesario para la vida: agua, tierras de cultivo, materiales de construcción, maderas, flora, fauna y abundantes productos de recolección.
Las investigaciones e interpretaciones realizadas señalan que este centro cívico ceremonial estuvo ligado a una organización social mayor que abarcaba alrededor de 60 asentamientos prehispánicos, y cuya cabecera de control político y económico posiblemente fue San Miguel Viejo, muy cerca de lo que hoy es la ciudad de San Miguel de Allende.
English:
Virgen de la Cañada: A ceremonial civic centre in the Laja river basin.
In the prehispanic era, Cañada de la Virgen was a ceremonial civic centre that reached its greatest development between 540 and 1050 a.C. In the excavations were found materials from the coasts of the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico, the West and the Basin of Mexico. In the abundant found ceramics the raised white type and the orange tones that are related to the queretanas lowlands and valleys of Hidalgo.
Here the gods and ancestors were worshiped, the stars were studied, mainly the moon, the sun and venus, from their registration and observation were determined the calendars that governed the ceremonial life, as well as the handling of the exchange cycles with nature, and productive activities such as agriculture, hunting and gathering.
Cañada de la Virgen is on a plateau surrounded by ravines on which rests a pond that should have been strategic for the foundation of the place, because with the water and the various resources of the ecosystem of plateaus,
ravines, and valleys, we had what was necessary to life: water, farmland, building materials, wood, flora, fauna, and abundant collection products.
The investigations and interpretations made indicate that his ceremonial civic center was linked to a larger social organization that encompassed around 60 pre-Hispanic settlements, and whose political and economic control was possibly at the site called San Miguel Viejo, very close to what today It is the city of San Miguel de Allende.
Erected by Consejo Nacional para la Cultura y las Artes de México (CONACULTA)-INAH.
Topics. This historical marker is listed in these topic lists: Anthropology & Archaeology • Man-Made Features • Native Americans.
Location. 20° 51.514′ N, 100° 55.64′ W. Marker is near San Miguel de Allende, Guanajuato. Marker can be reached from Route 67. The marker is the second marker to the right upon entering the archaeological site of Cañada de la Virgen. The archaeological site of Cañada de la Virgen is to the left when traveling north on State Road 67, some 30 km west of San Miguel de Allende. Touch for map. Marker is in this post office area: San Miguel de Allende GTO 37701, Mexico. Touch for directions.
Other nearby markers. At least 8 other markers are within walking distance of this marker. Ceremonial Road (within shouting distance of this marker); Complex A The House of the Thirteen Heavens
(within shouting distance of this marker); Observing the Stars (about 90 meters away, measured in a direct line); Burial 13 The hierarch and ancestral veneration (about 150 meters away); Layout and Architecture (about 180 meters away); Complex B: The House of the Longest Night (about 180 meters away); Complex D. The wind house. (The house of the wind) (about 180 meters away); Burial 18 The Decapitated Man (about 210 meters away). Touch for a list and map of all markers in San Miguel de Allende.
Regarding Cañada de la Virgen: A Ceremonial Civic Center in the Laja River Basin Marker. The previous marker had the following text:
Cañada de la Virgen: un centro cívico ceremonial en la cuenca de río Laja
En la epoca prehispánica Cañada de la Virgen fue un centro cívico ceremonial que alcanzó su mayor desarrollo durante los años 540
a 1050 d.C., sin que a la fecha haya sido posible determinar a que
cultura perteneció. En las excavaciones se encontraron materiales procedentes de las costas del océano pacífico y el golfo de México,
el occidente y la cuenca de México. En la abundante cerámica encontrada predomina el tipo Blanco Levantado y los tonos anaranjados que se relacionan con las tierras bajas que queretanas y los valles del Hidalgo.
Aquí se veneraba a los dioses y ancestros, se estudiaba a los astros, principalmente la Luna el Sol y Venus, y se determinaban
los calendarios que regían la vida ceremonial, así como los ciclos
de intercambio con la naturaleza, agricultura, caza y recolección.
Cañadas de la Virgen se encuentra sobre una meseta redeada de cañadas sobre la que descansa un estanque que debió ser estratégico para la fundación del lugar, pues con el agua y los variados recursos de este ecosistema de mesetas, cañadas y valles, se tenía lo necesario para el asentamiento: agua, tierras de cultivo, materiales de construcción, maderas, flora, fauna y abundantes productos de recolección.
Las investigaciones e interpretaciones realizadas señalan que este centro cívico ceremonial estuvo ligado a una organización social mayor que abarcaba alrededor de 60 asentamientos prehispánicos, y cuya cabecera de control político y económico posiblemente fue San Miguel El Viejo, ubicado muy cerca y al sur de lo que hoy es la ciudad de San Miguel de Allende.
English:
A ceremonial centre in the Laja river basin
In the Pre-Hispanic era Cañada de la Virgen
was a ceremonial civic centre which reached the height of its development between 540 and 1050 CE, it has not been possible to determine what culture it belonged to. Materials from the Pacific and Gulf coastal regions as well as from the west and the basin of Mexico were found during excavations. Raised White ceramics and the orange tones characteristic of the Queretaro lowlands and Hidalgo valleys predominate among the abundant ceramics found here.
Cañada de la Virgen was a religious centre in which gods and ancestors were worshipped and the stars studied, mainly the moon, the sun and venus. The calendars which governed ceremonial life were decided here, as well as those relating to nature: for agriculture, hunting and gathering.
Cañada de la Virgen is surrounded by gorges,
located on a plateau which holds a pond that must have been strategic for foundation of the place as, with water and the various resources of this ecosystem – plateaus, gorges and valleys - the settlement had everything required: water, farm land, construction materials, wood, flora, fauna, and abundant gathering produce.
The investigations and analyses carried out indicate that his ceremonial civic centre was linked to a greater organization which spread over approximately 60 Pre-Hispanic settlements. The governing centre, or political and administrative centre, may have been
San Miguel El Viejo (Old San Miguel), situated just south of what is today known as the city of San Miguel de Allende.
Credits. This page was last revised on September 1, 2020. It was originally submitted on May 23, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. This page has been viewed 154 times since then and 7 times this year. Photos: 1. submitted on August 30, 2019, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. 2. submitted on May 23, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. 3. submitted on August 30, 2019, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. 4. submitted on May 23, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. 5. submitted on August 30, 2019, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. 6. submitted on June 6, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana.