Near San Juan Opico, San Salvador, El Salvador — Central America (West Coast)
The San Salvador Volcano Complex
Centroamérica se halla en una zona de contacto entre dos placas tectónicas: la Placa de Cocos y la Placa del Caribe, que interactúan creando una cinta volcánica llamada Cinturón de Fuego del Pacífico. Así, podemos encontrar volcanes del oriente hasta el poniente del país.
El Volcán de San Salvador
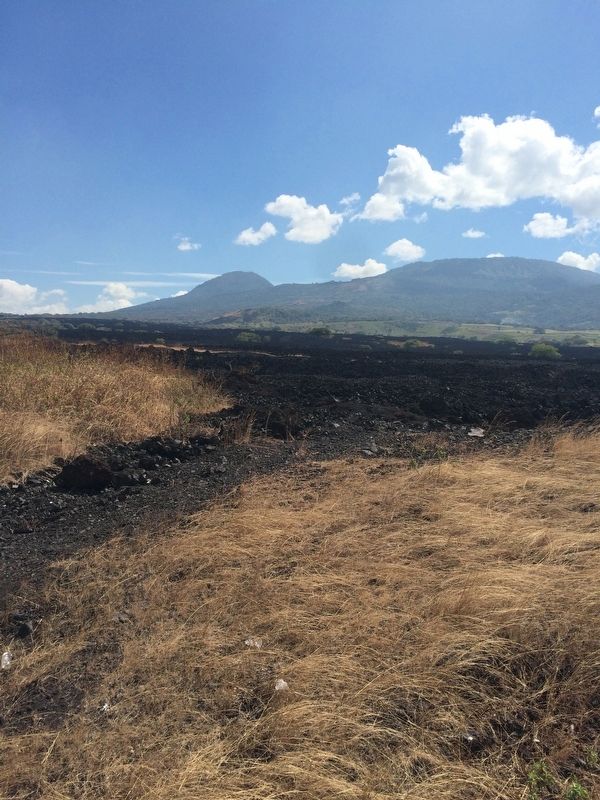
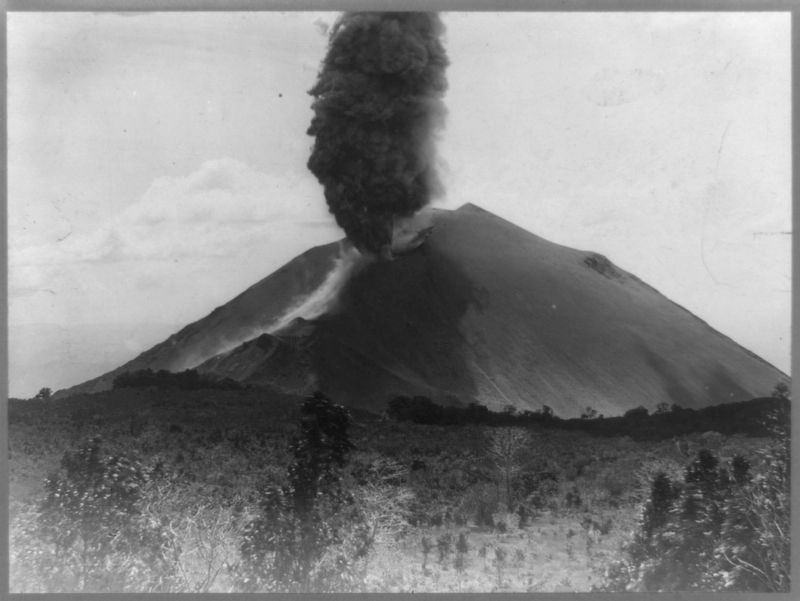
El Volcán de San Salvador, con una altura de 1960 msnm. Se halla señoreando la capital San Salvador. Está conformado por los restos de erupciones múltiples: una silueta de elevada y aguda cumbre en su parte oriental (El Picacho, 1960 m.), una parte central más chata con un gran cráter (El Boquerón, 1893.39 m.) y una cima menos prominente al noroeste, llamada El Jabalí. Todo el complejo abarca una superficie de 110 km2.
El Volcán ha hecho erupción en varias ocasiones en los últimos 70.000 años, a través de su cráter central, así como por fisuras en sus flancos. En un radio de 10 kms. alrededor se encuentran diversos conos de escoria-cenizas y cráteres de explosión.
Sabría usted que: Prácticamente todo el subsuelo del país (más de un 90%) está formado por materiales volcánicos.
Pie de dibujos:
Placas tectónicas alrededor de Centroamérica (Fuente: wikimedia.org)
El Volcán San Salvador y su complejo volcánico
(fuente: Explosive volcanic history and hazard zonation maps of Boquerón Volcano, D. Ferrés & al.)
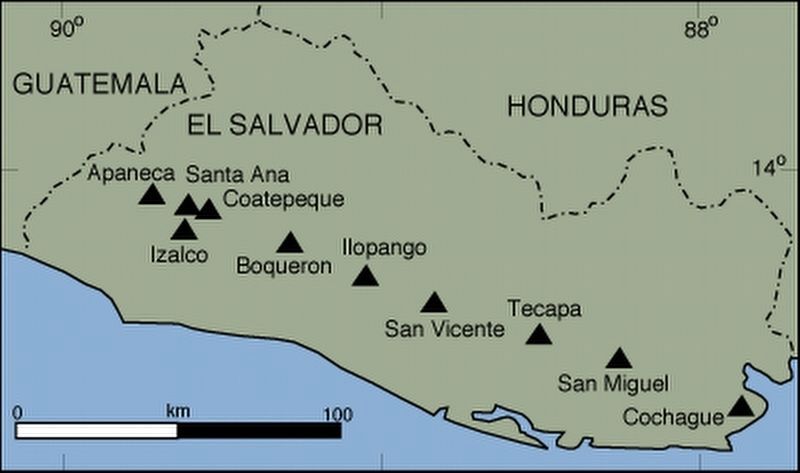
Los principales volcanes de El Salvador (Fuente: conacyt.gov.sv)
Lagoon, the Argentina Forest, and El Playón Volcano Crater and its surroundings. Central America is located in a contact zone between two tectonic plates: the Cocos Plate and the Caribbean Plate, which interact creating a volcanic belt called the Pacific Fire Belt. Thus, we can find volcanos across the length of the country from east to west.
The Volcano of San Salvador
The Volcano of San Salvador has a height of 1960 masl (meters above mean sea level). It overlooks the capital of San Salvador. It is formed by the remains of multiple eruptions: a silhouette with a high and sharp summit on its eastern part (El Picacho, 1960 m.), a more flat central part with a large crater (El Boquerón, 1893.39 m.) And a prominent lower summit, called El Jabalí (The Wild Boar). The whole complex covers an area of 110 square kilometers.
The volcano has erupted several times in the last 70,000 years, through both its central crater as well as through fissures on its flanks. Within a radius of 10 kms. around it are various cones of slag-ash and explosive craters.
Did you know? Practically all the subsoil of the country (more than 90%) is formed by volcanic materials.
Captions:
The tectonic plates of Central America (Source: wikimedia.org)
Volcano San Salvador and its volcanic complex
(source: Explosive Volcanic History and Hazard Zonation
maps of Boquerón Volcano, D. Ferrés, et. al)
The main volcanoes of El Salvador (Source: conacyt.gov.sv)
Erected by Alcaldía de San Juan Opico, Apoyo Urbano, AMUVASAN y la Unión Europea.
Topics. This historical marker is listed in this topic list: Environment. A significant historical year for this entry is 1917.
Location. 13° 48.269′ N, 89° 19.74′ W. Marker is near San Juan Opico, San Salvador. Marker is on Carretera Interamericana (CA-1). The marker is to the left on the Interamerican Highway, some kilometers before arriving to the town of Quezaltepeque. Touch for map. Marker is in this post office area: San Juan Opico, San Salvador CP 0515, El Salvador. Touch for directions.
Other nearby markers. At least 8 other markers are within 14 kilometers of this marker, measured as the crow flies. Joya de Cerén (approx. 4 kilometers away in La Libertad); Indigo Production at San Andrés (approx. 6.3 kilometers away in La Libertad); Abandonment of the San Andrés Archaeological Site (approx. 6.4 kilometers away in La Libertad); San Andrés was an extensive prehispanic settlement (approx. 6.5 kilometers away in La Libertad); San Andrés Archaeological Site (approx. 6.5 kilometers away in La Libertad); Structure 7 at San Andrés Archaeological Site (approx. 6.6 kilometers away in La
Libertad); El Boqueron National Park (approx. 9.5 kilometers away in La Libertad); Juan Pablo Duarte (approx. 13.4 kilometers away).
Credits. This page was last revised on September 13, 2018. It was originally submitted on August 20, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana. This page has been viewed 315 times since then and 39 times this year. Photos: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. submitted on August 20, 2017, by J. Makali Bruton of Accra, Ghana.